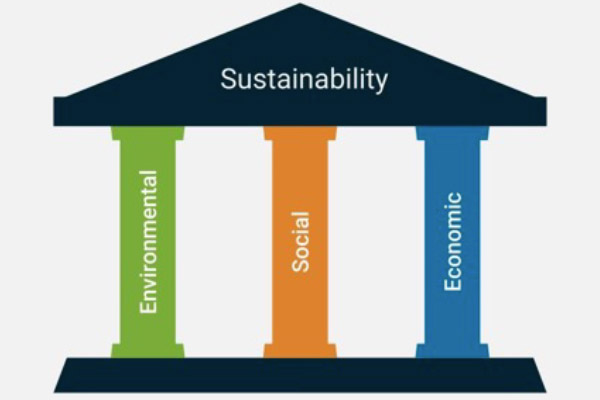
The three interconnected dimensions of sustainability:
- Environmental Sustainability: This pillar focuses on the conservation and preservation of natural resources, ecosystems, and biodiversity. It involves minimizing environmental impacts such as pollution, habitat destruction, and depletion of resources. Key aspects include reducing carbon emissions, conserving water and energy, promoting renewable energy sources, and protecting ecosystems.
- Social Sustainability: Social sustainability emphasizes the well-being, equity, and social justice of communities and individuals. It involves addressing social issues such as poverty, inequality, access to healthcare and education, labor rights, and community engagement. Organizations pursuing social sustainability aim to create inclusive workplaces, support local communities, and ensure fair treatment and opportunities for all stakeholders.
- Economic Sustainability: Economic sustainability focuses on long-term economic viability and prosperity while considering the needs of current and future generations. It involves practices that promote economic growth, stability, and resilience without compromising environmental or social objectives. This pillar encompasses factors such as financial performance, profitability, innovation, resource efficiency, and responsible investment.